|
6- Types of Electrical Boxes
There are many types of boxes used in a
conduit installation. The application
and site conditions determine the type of box used. The electrical boxes can
be divided to:
- The outlet boxes,
- Device boxes,
- Pull and junction boxes.
The following is a list of the more common
boxes and a brief description of their intended use.
First: Outlet Boxes
The outlet boxes with the correct fittings
be installed at the following locations:
- Each conductor splice point,
- Each outlet, switch point, or junction
point,
- Each pull point for the connection of
conduit and other raceways,
- Transitions from conduit to open cables.
- A wide variety of standard metal and nonmetallic
electrical or outlet boxes are available commercially for installing switches
and receptacles, connecting lighting fixtures, and protecting splices. Only
the most commonly used boxes and their features are discussed and illustrated
in this course.
- The type of enclosures used as outlet and
device boxes for supporting, enclosing and securing wiring devices such as
switches, receptacles or other equipment on the same yoke or strap are
available in various sizes and shapes. These enclosures may be used in one,
two, three or more gang types.
6.1
Rectangular outlet boxes
Rectangular
outlet box
- Rectangular
outlet boxes are
intended for installing a single switch or a duplex receptacle. Also called device
boxes, they
are normally mounted vertically in walls by fastening them to wall studs in
new construction.
- Rectangular
outlet boxes
can be ganged together with matching boxes to provide a single box with twice
the volume. After removing the opposing removable sides of each box, they are
fastened together with screws to form one rigid unit. Ganged boxes can accept
two switches or two duplex receptacles with their associated wiring.
6.2
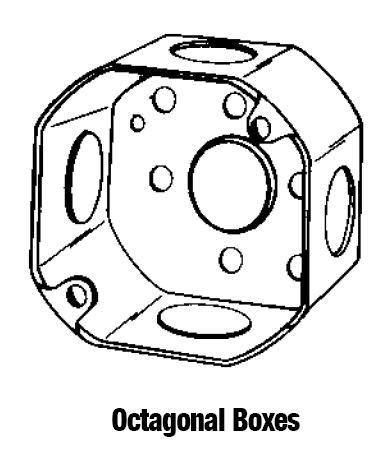
Octagonal Outlet Boxes
- An octagon box often referred to as a
“fixture box”, connects light fixtures. Octagon boxes have cover plates to protect
conductors when the box is used as a junction box. Table 314-16(a) lists the
sizes of boxes with or without devices, but only #14 through #6 wires may be
used. Octagon boxes are available in different sizes to accommodate cable
clamps, fitting, and devices (switches or receptacles).
- These boxes are
conventionally measured diagonally, where their actual dimensions are 4 in.,
but they have nominal 4-in. dimensions when measured between their flat
sides. They can be fastened to ceiling joists or studs with nails or screws,
or can be supported by telescoping metal braces that extend to fit between
adjacent joists. These boxes are frequently used to support luminaires if
there are studs or hickeys in the box, on the box covers, or on cross straps.
Notes for fixture boxes:
- Boxes for supporting lighting fixtures and
ceiling paddle fans are available in the round and octagonal types.
- Generally, device boxes are not acceptable
for securing or supporting lighting fixtures. One of the reasons is that
device boxes have 6-32 tapped screw holes and round or octagonal boxes have
8-32 tapped screw holes to support the weight of the lighting fixture.
6.3
Round Ceiling Pan Boxes
- Round
ceiling pan boxes with
diameters of 3.25 in. have applications similar to those of octagonal boxes
because they can be mounted on walls or ceilings to support light fixtures.
Round boxes with depths of 0.5 in. have volumes of 4 in.3, and
those with depths of 0.75 in. have volumes of 5.5 in.3. A choice
of internal cable clamps is offered with these boxes, and they can accept
round covers that fit both round and octagonal boxes.
6.4
Square Outlet Boxes
- The square box measures four
inches by four inches. They are
large enough to gang two switches or two duplex receptacles in one box or to
protect cable splices.
- It
encloses switches, thermostats, timers and receptacles. They have more
cubic-inch volume than octagon boxes and allow more conductors to be
installed. They also have accessories such as plaster (mud) rings to mount
fixtures or devices. It also functions as a junction box or pull box.
- Where a square metal box is used, it may be
used for the support of a fixture or device, depending on the type of raised
cover used. These covers are often referred to as “plaster” or “mud” rings.
- Square boxes are also
normally mounted vertically in walls by nailing them to studs during original
construction. A wide selection of cover plates is available for these boxes,
with different cutouts to admit the toggles of strap-mounted switches or to
expose both outlets of strap-mounted dual receptacles. Single switches or
duplex receptacles can be installed in these boxes if an adapter cover plate
with a centrally located cutout is used.
6.5 The Utility Box
- The utility box or outlet box mounts on
surfaces. It is often referred to as a
“handy box.” The utility box encloses
switches, receptacles, thermostats, or push button units. The box is a minimum of 1.5 inches deep.
Boxes must meet the minimum cubic inch capacity per number of conductors per
Table 314-16(a) and Table 314-16(b) of Article 314 in the NEC. Connect conduit to any one of the knockout
holes in the box. This type of box is used for exposed work.
6.6 The Conduit Device Box
- A conduit device box installs in drywall. The sides can be removed to enlarge it by
attaching another box. This is
referred to as "ganging the boxes."
A conduit device box installs in offices and homes for switches and
receptacles.
6.7 The masonry box
- The masonry box is special conduit device
boxes. The masonry box installs in concrete block and brick walls. Available in various sizes, the masonry box
does not enlarge.
6.8 The weatherproof box
- The
weatherproof box is special conduit device boxes and used outside and in damp
or wet areas. The weatherproof box is
made of heavy cast metal and has a threaded hub to connect to conduit.
|






.JPG)
.JPG)



Impressive post, it is very helpful to me. I learn a lot about electrical boxes and I should apply this to my project. :D
ReplyDelete